- IT Services
- Cryptography
Cryptography
-
Cryptography is not just a technical tool — it’s a cornerstone of digital trust in our connected world. From protecting your personal messages to securing trillion-dollar transactions, cryptography keeps the digital world running safely.
-
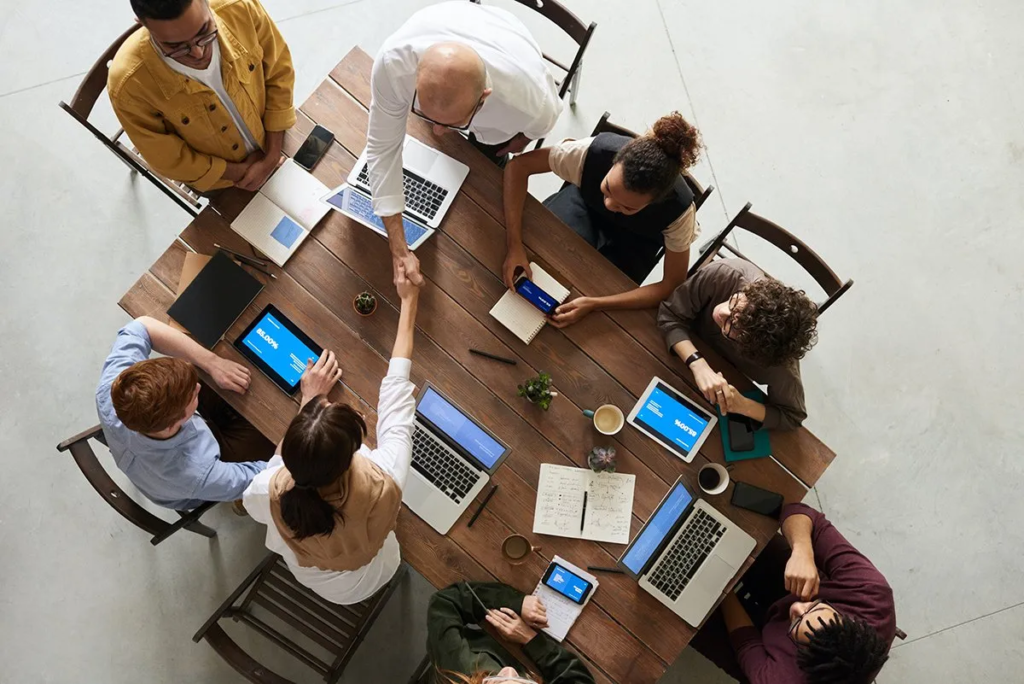
Core Concepts of Cryptography
- Encryption : Converting readable data (plaintext) into an unreadable form (ciphertext).
- Decryption : Converting ciphertext back into plaintext using a key.
- Keys : Unique values used in encryption/decryption; can be public or private.
- Symmetric Cryptography : Same key for both encryption and decryption.
- Asymmetric Cryptography{ Uses a public key to encrypt and a private key to decrypt.
- Hashing : Converts data into a fixed-length value; cannot be reversed.
- Digital Signatures : Proves the authenticity and integrity of digital messages.
Benefits of choosing BIITS for Cryptography
Data Privacy – Prevents unauthorized access to sensitive data.
Data Integrity – Ensures information hasn’t been altered in transit.
Authentication – Verifies the identity of users or systems.

Non-repudiation – Ensures a sender cannot deny the authenticity of their message.
Secure Communication – Enables safe transmission over insecure networks.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between encryption and hashing?
Encryption can be reversed (decrypted) with a key. Hashing is one-way and is used mainly for verifying data integrity.
Is cryptography only used in IT and cyber security?
No. It’s also used in secure voting, digital forensics, and more.
What are real-life examples of cryptography?
-SSL/TLS in websites (https://) -WhatsApp end-to-end encryption -ATM PIN verification
Can encrypted data be hacked?
In theory, yes — but with strong algorithms and keys, it’s extremely difficult without access to the key.

Need help with UI Designing?
